MongoDB
MongoDB is a general purpose, document-based, distributed database built for modern application developers and for the cloud era.
Create a MongoDB Database#
All MongoDb servers are 100% dedicated to your environment.
- Click on the Create Service button at the top right of your environment.
- Click on the From Catalog tab at the top right.
- Click on the MongoDB option in the list.
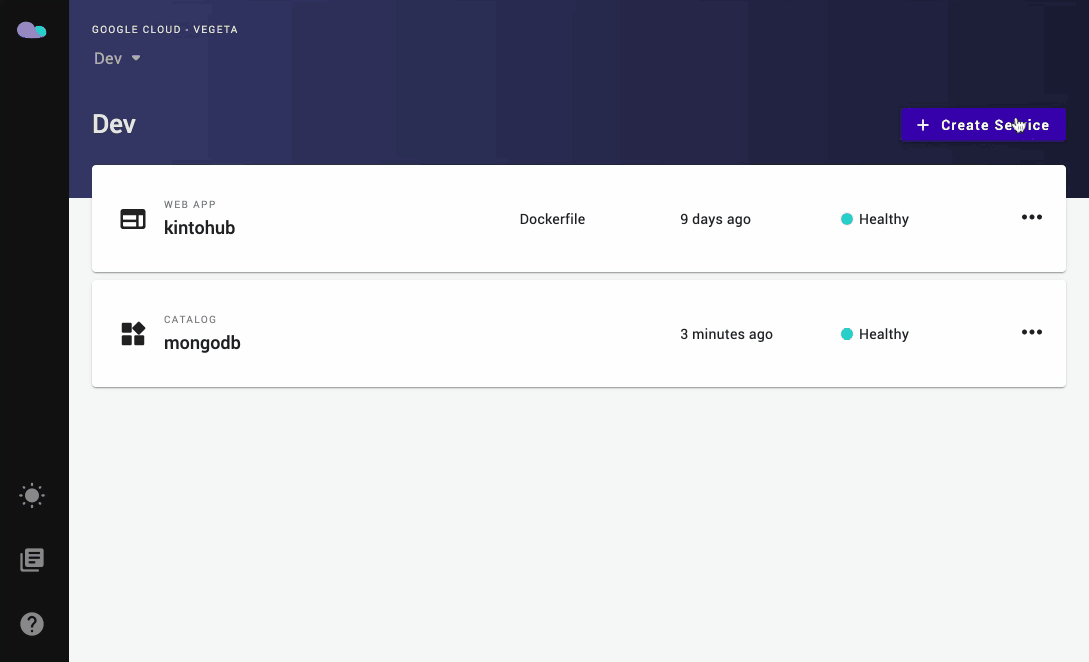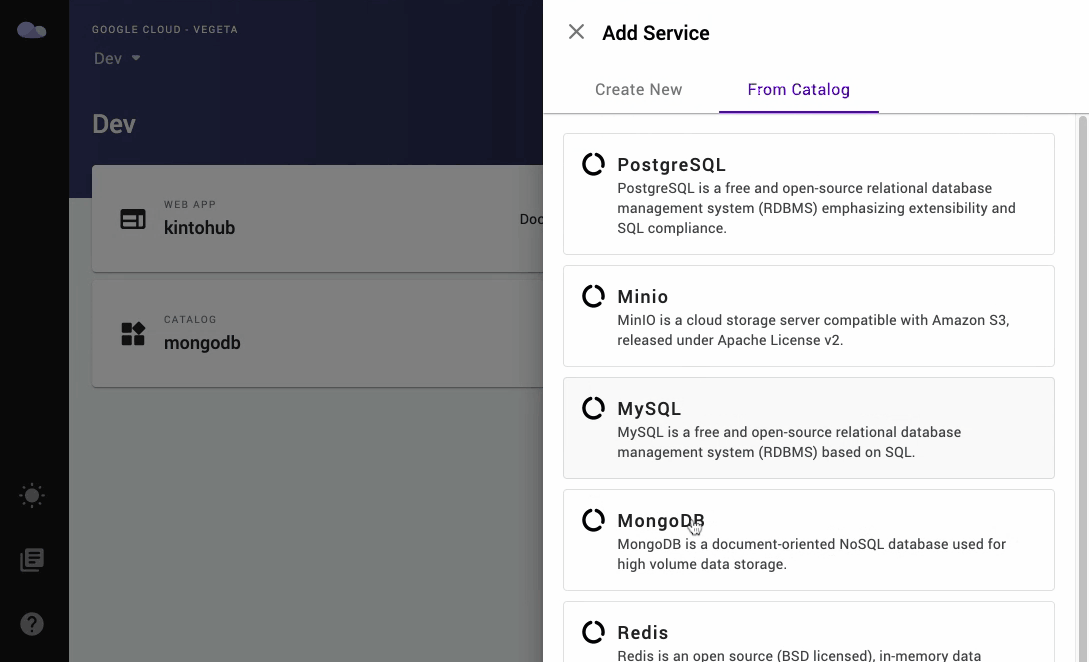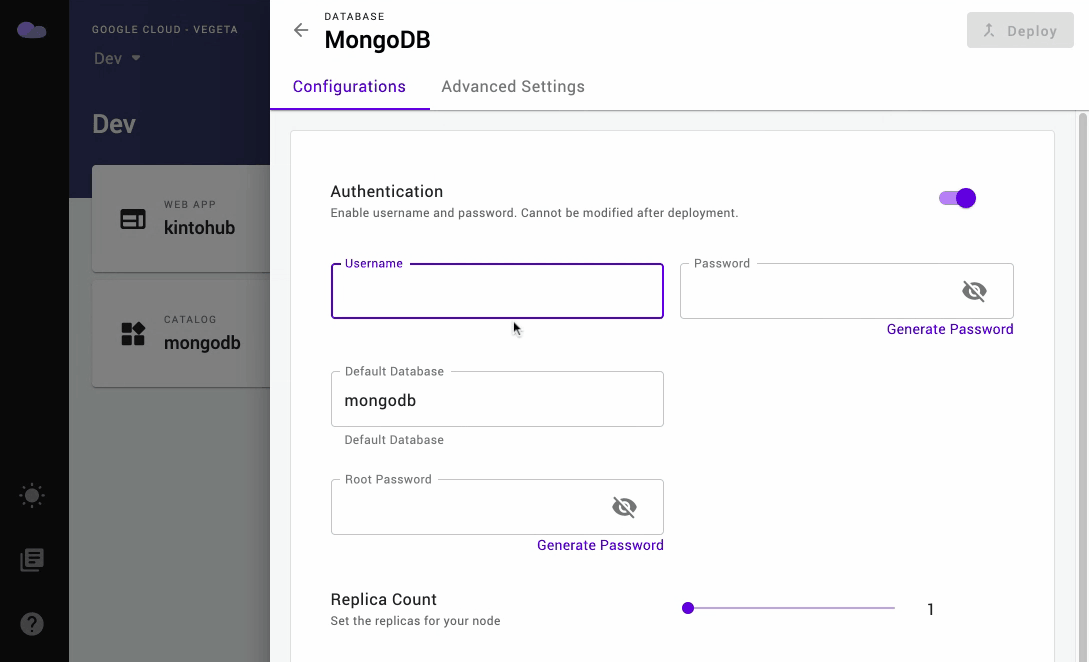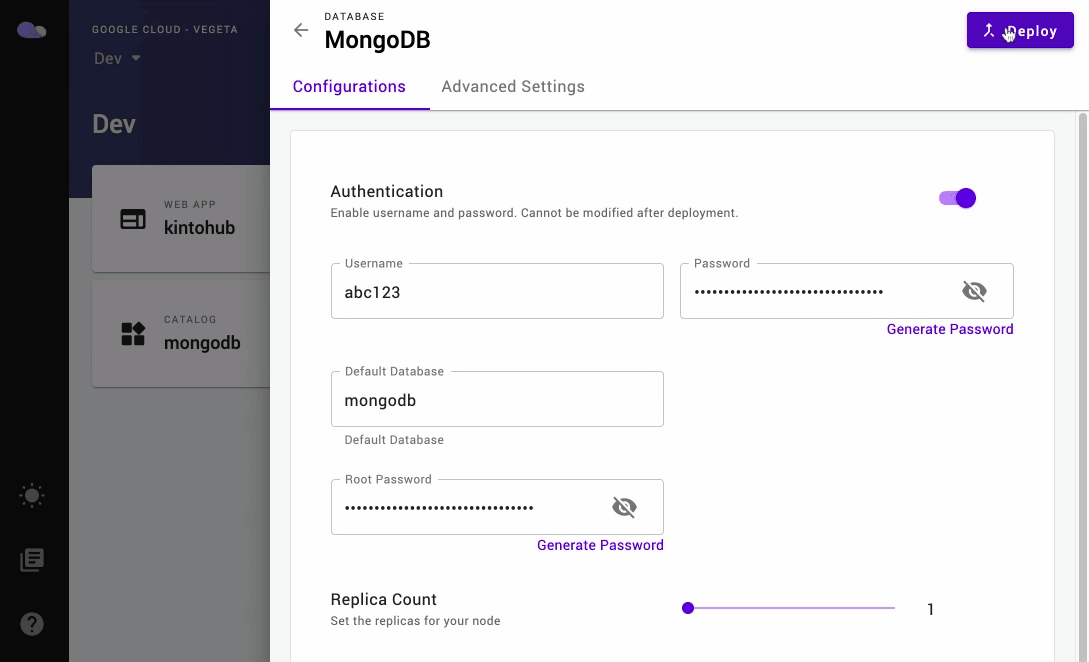
- Optionally enable Authentication and input or generate your
Username,PasswordandRoot Password. - Click on the Deploy button at the top right and wait until the release is successful.
- Once deployed, click on the Access Tab to read the access related options.
Access Your MongoDB Instances#
Access from service running on KintoHub#
You may only access your MongoDB Instance from services running in the same environment. Learn more about how to connect to your MongoDB Instance under the Access Tab.
Access from local machine#
You can install the Kinto CLI and run kinto teleport from a .git folder that has been deployed on KintoHub with a MongoDB database.
Using the tunnel that is created with this command, you can use any 3rd party mongo client to connect or the mongo cli.
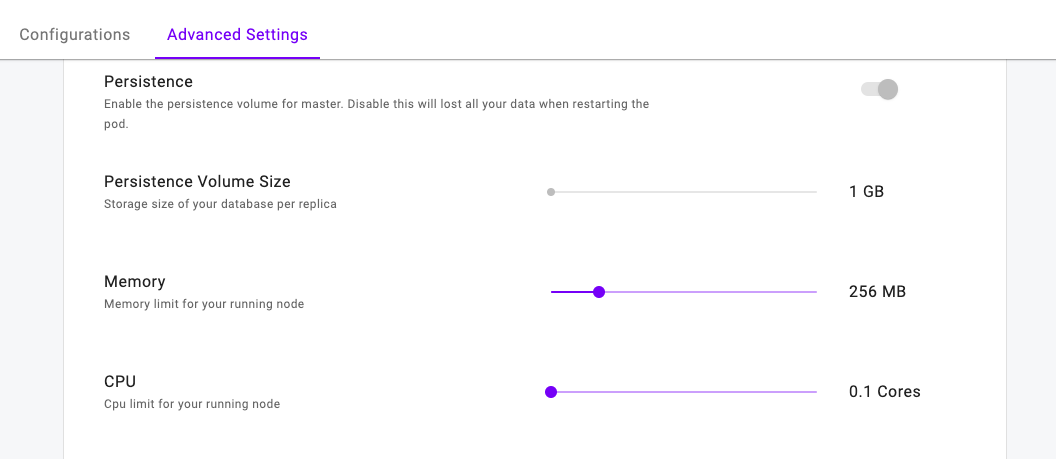
MongoDB Advanced Options#
Replica Count#
Increasing your replicas will create Highly Available MongoDB instances.
You can increase or decrease your replicas under the Configurations tab when creating a MongoDB service.
It's recommended to have at least 3 replicas in production environments or any environments you wish to decrease the chances of downtime.
Read more about replicas here.
(Storage) Persistence#
MongoDB has an optional (Storage) Persistence and Volume Size options available under the Advanced Options Tab.